Foote cone and belding grid – Embark on a journey into the realm of advertising with the Foote Cone & Belding (FCB) Grid, a pioneering model that has revolutionized our understanding of consumer behavior. This comprehensive guide delves into the history, dimensions, applications, and limitations of this influential grid, providing invaluable insights for marketers and advertisers alike.
The FCB Grid, developed by the renowned advertising agency Foote, Cone & Belding, serves as a framework for analyzing consumer behavior by considering four key dimensions: involvement, motivation, ability, and knowledge. These dimensions interact in complex ways, influencing how consumers process and respond to advertising messages.
Introduction

The Foote, Cone & Belding (FCB) Grid is a strategic planning tool used in advertising to analyze the target audience and develop effective marketing campaigns. It was developed by Rosser Reeves, an advertising executive at FCB, in the 1960s.
The FCB Grid is a 2×2 matrix that plots the target audience’s motivations (rational or emotional) against their level of involvement (high or low). This framework helps advertisers understand the most effective way to reach and persuade their target audience.
History and Development
The FCB Grid was first introduced in Reeves’ book, Reality in Advertising. Reeves argued that advertising should focus on a single, clear message that would motivate the target audience to take action. The FCB Grid provided a framework for developing such messages.
The FCB Grid has been widely used in advertising for decades. It has been adapted and updated over time, but its basic principles remain the same.
Dimensions of the FCB Grid

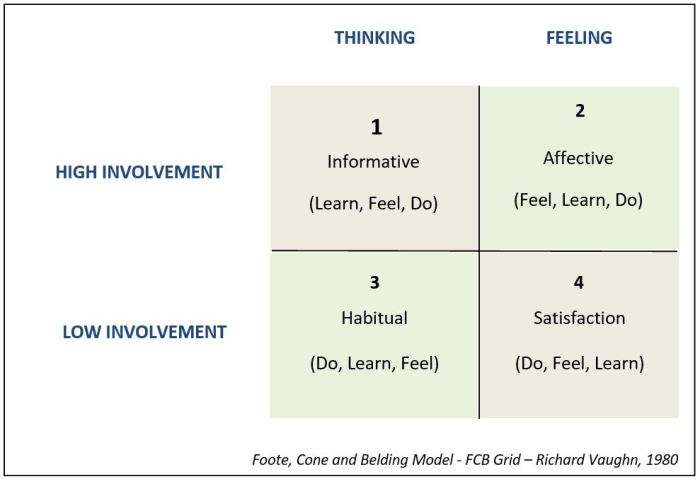
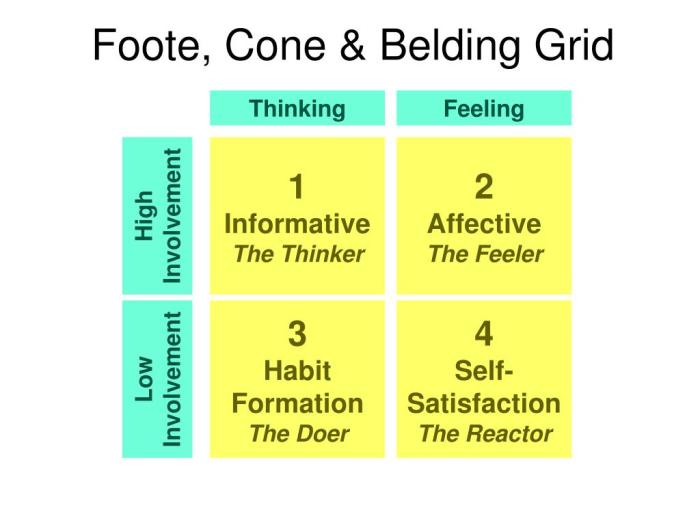
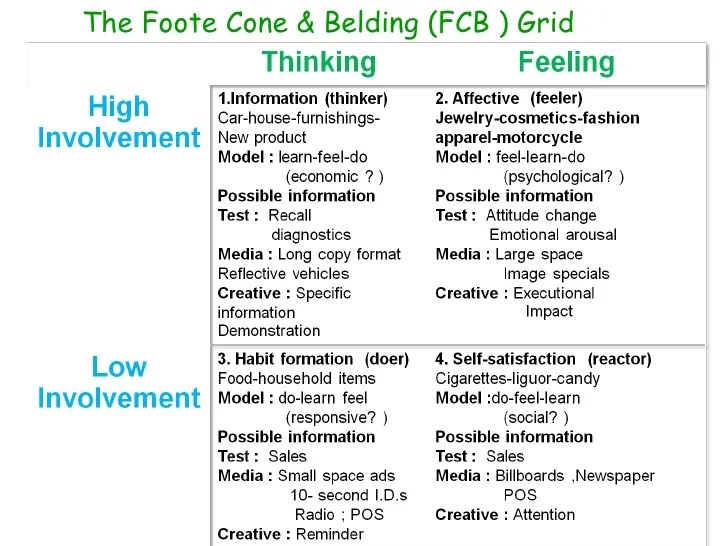
The FCB Grid is a four-dimensional framework that helps marketers understand and influence consumer behavior. The four dimensions are:
- Involvement
- Motivation
- Ability
- Knowledge
These dimensions interact in complex ways to influence consumer behavior. For example, a consumer who is highly involved in a product category is more likely to be motivated to purchase the product, and they are also more likely to have the ability and knowledge to do so.
Involvement
Involvement is the degree to which a consumer is interested in a product or service. Involvement can be either high or low. High-involvement products are typically those that are expensive, important, or risky. Low-involvement products are typically those that are inexpensive, unimportant, or non-risky.
Motivation, Foote cone and belding grid
Motivation is the force that drives a consumer to take action. Motivation can be either intrinsic or extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation is the desire to do something for its own sake, while extrinsic motivation is the desire to do something in order to obtain a reward or avoid a punishment.
Ability
Ability is the consumer’s perception of their ability to perform a task. Ability can be either high or low. High-ability consumers are those who believe that they can easily perform a task, while low-ability consumers are those who believe that they cannot perform a task easily.
Knowledge
Knowledge is the consumer’s understanding of a product or service. Knowledge can be either high or low. High-knowledge consumers are those who have a lot of information about a product or service, while low-knowledge consumers are those who have little information about a product or service.
Applying the FCB Grid in Advertising
The FCB Grid is a valuable tool for advertisers to create effective and targeted advertising campaigns. It provides a framework for understanding the different dimensions of a brand and its target audience, allowing advertisers to develop messages that resonate with consumers on an emotional level.
One of the key benefits of the FCB Grid is that it helps advertisers to focus on the emotional connection between the brand and the consumer. By understanding the consumer’s motivations, values, and aspirations, advertisers can create messages that are relevant and meaningful to them.
This can lead to increased brand awareness, engagement, and sales.
Examples of Successful Applications
Many brands have successfully used the FCB Grid to develop effective advertising campaigns. Here are a few examples:
- Nike: Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign is a classic example of how the FCB Grid can be used to create a powerful emotional connection with consumers. The campaign focuses on the consumer’s desire to overcome challenges and achieve their goals, and it has helped Nike to become one of the most iconic brands in the world.
- Apple: Apple’s “Think Different” campaign is another example of how the FCB Grid can be used to create a strong emotional connection with consumers. The campaign focuses on the consumer’s desire to be creative and independent, and it has helped Apple to become one of the most successful companies in the world.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign is a more recent example of how the FCB Grid can be used to create a successful advertising campaign. The campaign focuses on the consumer’s desire to connect with others, and it has helped Coca-Cola to increase sales and brand awareness.
The Foote Cone and Belding Grid is a popular framework for understanding consumer behavior. It can be used to analyze a wide range of marketing and advertising campaigns, including those for the best UGS courses at UT Austin ( best ugs courses ut austin ). The grid helps marketers identify the key drivers of consumer behavior and develop strategies to influence them.
It is a valuable tool for any marketer looking to improve the effectiveness of their campaigns.
Limitations of the FCB Grid
The FCB Grid, while a useful tool for understanding consumer behavior, has some limitations.
One limitation is that it can be overly simplistic. It assumes that consumer behavior is always rational and logical, which is not always the case. Consumers are often influenced by emotions, social factors, and other irrational factors.
Using the FCB Grid with Other Models
Another limitation is that the FCB Grid does not take into account the role of advertising in shaping consumer behavior. Advertising can create awareness, build brand loyalty, and change attitudes. The FCB Grid does not account for these effects.
Despite these limitations, the FCB Grid can be a useful tool for understanding consumer behavior. It can help advertisers develop more effective marketing campaigns by providing insights into consumer needs and motivations.
Case Studies
The FCB Grid has been employed in numerous successful advertising campaigns across various industries. By understanding the target audience’s motivations and behavior, advertisers can create effective messages that resonate with consumers.
Let’s explore a few real-world case studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of the FCB Grid in practice:
Nike’s “Just Do It” Campaign
Nike’s iconic “Just Do It” campaign, launched in 1988, exemplifies the power of the FCB Grid. The campaign targeted active individuals who desired to push their limits and achieve their fitness goals. Nike positioned itself as the brand that understood and supported their aspirations, creating a strong emotional connection with the audience.
The campaign’s success can be attributed to its focus on the “feeling” and “action” quadrants of the FCB Grid. The message inspired consumers to take action and embrace their potential, resulting in a significant increase in brand recognition and sales.
Dove’s “Real Beauty” Campaign
Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign, launched in 2004, challenged societal beauty standards and celebrated the diversity of women. The campaign targeted women who felt insecure about their appearance and aimed to redefine the concept of beauty.
Dove effectively utilized the “thinking” and “feeling” quadrants of the FCB Grid. The campaign used real women in its advertisements, showcasing their unique qualities and experiences. This approach resonated with the target audience, fostering a sense of relatability and self-acceptance.
The “Real Beauty” campaign resulted in increased brand loyalty and sales, proving the effectiveness of connecting with consumers on an emotional and cognitive level.
Alternative Models
The FCB Grid is not the only model for understanding consumer behavior in advertising. Other models, such as the AIDA model and the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM), offer different perspectives and can be more appropriate in certain contexts.
AIDA Model
The AIDA model is a classic advertising model that describes the stages a consumer goes through when making a purchase decision: Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action. This model emphasizes the importance of capturing the consumer’s attention and then gradually building their interest and desire until they take action.
The AIDA model is simple and easy to understand, making it a good choice for advertising campaigns with clear and straightforward goals. However, it can be less effective for complex products or services that require more in-depth consideration.
Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM)
The ELM proposes that consumers process information in two different ways: centrally and peripherally. Central processing involves actively thinking about the message and evaluating its arguments, while peripheral processing focuses on superficial cues, such as the attractiveness of the ad or the celebrity spokesperson.
The ELM suggests that the effectiveness of an advertising message depends on the consumer’s motivation and ability to process information. When consumers are highly motivated and have the ability to process information centrally, they are more likely to be persuaded by logical arguments and evidence.
When consumers are less motivated or have limited ability to process information, they are more likely to be influenced by peripheral cues.
Conclusion

The FCB Grid is a foundational tool that has played a pivotal role in advertising for decades. It offers a systematic approach to understanding and connecting with consumers, enabling advertisers to craft compelling and persuasive messages. The grid’s emphasis on involving the consumer in the advertising process remains highly relevant in today’s advertising landscape.The
modern advertising environment is characterized by increased fragmentation and personalization. Consumers are bombarded with countless messages, and advertisers need to find ways to cut through the clutter and connect with their target audiences. The FCB Grid provides a framework for creating advertising that is relevant, meaningful, and engaging.
By understanding the consumer’s needs, motivations, and values, advertisers can create ads that resonate on a deeper level and drive desired outcomes.
Ongoing Relevance
Despite the evolution of advertising channels and technologies, the FCB Grid’s core principles remain essential for effective advertising. By focusing on the consumer and their needs, advertisers can create campaigns that are more likely to be successful in today’s competitive marketplace.
Importance in the Modern Landscape
The FCB Grid’s importance lies in its ability to help advertisers navigate the complexities of the modern advertising landscape. By providing a structured approach to understanding consumers and developing effective advertising strategies, the grid empowers advertisers to maximize their impact and achieve their business objectives.
FAQ Corner: Foote Cone And Belding Grid
What is the FCB Grid?
The FCB Grid is a model developed by Foote, Cone & Belding to analyze consumer behavior and guide advertising campaigns.
What are the four dimensions of the FCB Grid?
The four dimensions are involvement, motivation, ability, and knowledge.
How can the FCB Grid be used in advertising?
Advertisers can use the FCB Grid to develop targeted campaigns that address the specific needs and characteristics of their target audience.
What are the limitations of the FCB Grid?
The FCB Grid may not be suitable for all advertising contexts and can be criticized for its complexity and reliance on subjective assessments.