Using the following equation for the combustion of octane, C8H18 + 12.5O2 → 8CO2 + 9H2O, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of octane combustion, unraveling its energy release, product formation, and environmental implications.
This equation serves as a cornerstone for understanding the combustion process, providing a quantitative framework for analyzing the chemical reactions involved and their impact on various aspects, including energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Combustion of Octane
Combustion is a chemical process that involves the rapid reaction of a substance with oxygen, releasing heat and light. Octane, a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C 8H 18, is a common fuel used in gasoline engines. When octane undergoes combustion, it reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
The chemical equation for the combustion of octane is as follows:
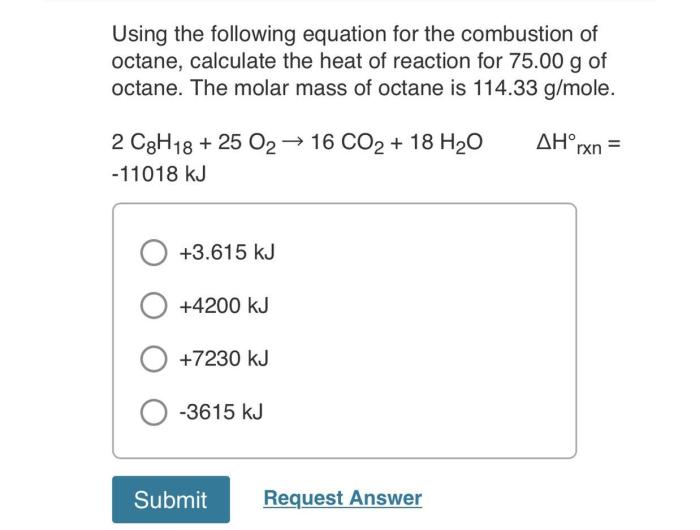
C8H 18+ 25O 2→ 16CO 2+ 18H 2O + energy
The combustion of octane is a complex process that involves several factors, including the temperature, pressure, and availability of oxygen. The rate of combustion is also affected by the presence of catalysts, which are substances that can speed up or slow down the reaction.
Energy Released by Octane Combustion
The combustion of octane releases a significant amount of energy, which is why it is used as a fuel in gasoline engines. The amount of energy released during combustion depends on the stoichiometric ratio, which is the ratio of fuel to air in the combustion mixture.
The stoichiometric ratio for octane is 14.7:1, which means that for every 14.7 grams of octane, there must be 1 gram of air.
The energy released by the combustion of octane is also affected by the efficiency of the engine. The efficiency of an engine is a measure of how much of the energy released during combustion is converted into useful work. The efficiency of gasoline engines typically ranges from 20% to 30%.
Products of Octane Combustion
The major products of octane combustion are carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Water is a harmless byproduct of combustion, but it can cause problems if it condenses in the engine.
In addition to carbon dioxide and water, octane combustion also produces a number of other pollutants, including nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons. Nitrogen oxides are a major contributor to smog, while carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that can cause health problems.
Applications of Octane Combustion
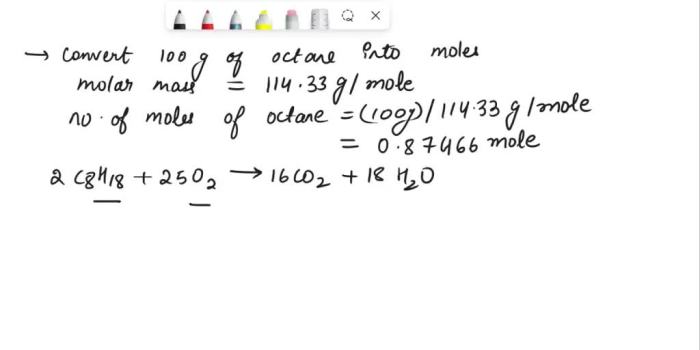
Octane combustion is used in a variety of applications, including gasoline engines, diesel engines, and jet engines. Octane is a good fuel for gasoline engines because it has a high octane rating, which means that it is resistant to knocking.
Knocking is a condition that can occur in gasoline engines when the fuel ignites too early, causing a loss of power and efficiency.
Octane is also used in diesel engines, but it is not as common as diesel fuel. Diesel fuel has a lower octane rating than octane, but it is more energy-dense, which means that it can provide more power for the same volume of fuel.
Safety Considerations for Octane Combustion

Octane is a flammable liquid that can be dangerous if not handled properly. It is important to store octane in a cool, dry place away from sources of heat and ignition. Octane should also be handled with care to avoid spills and leaks.
In case of a spill or leak, octane should be cleaned up immediately. Octane can be absorbed with a spill kit or by using sand or dirt. The contaminated material should be disposed of properly.
Question Bank: Using The Following Equation For The Combustion Of Octane
What is the significance of the stoichiometric ratio in octane combustion?
The stoichiometric ratio represents the ideal proportion of octane to oxygen required for complete combustion. Abweichungen from this ratio can affect the energy release and product formation, influencing factors such as fuel efficiency and emissions.
How does octane combustion contribute to environmental pollution?
Incomplete combustion of octane can lead to the formation of harmful pollutants, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions contribute to air pollution, climate change, and adverse health effects.