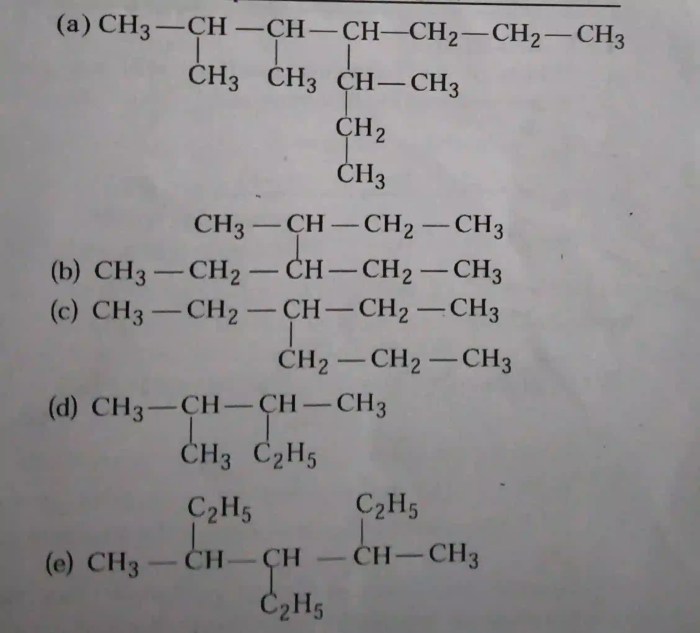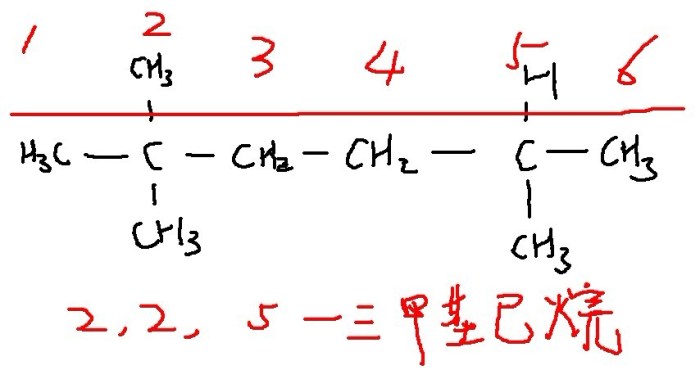Draw the structural formula of 5 ethyl 2 methyloctane – Delving into the intricacies of organic chemistry, we embark on a journey to decipher the structural formula of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane, an alkane with a captivating array of properties and applications. This guide will illuminate the IUPAC nomenclature, isomerism, physical and chemical characteristics, and practical uses of this fascinating compound, providing a comprehensive understanding of its molecular makeup and significance.
The structural formula of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane, a branched-chain alkane, serves as the cornerstone of our exploration. Its unique arrangement of carbon atoms and functional groups bestows upon it distinct properties that shape its behavior and utility.
5-Ethyl-2-Methyloctane
-ethyl-2-methyloctane is an organic compound with the molecular formula C12H26. It is a branched-chain alkane, meaning that its carbon atoms are not all arranged in a straight line. The IUPAC name for 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane is 2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)octane.
Structural Formula
The structural formula of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane is:“`CH3-CH(CH3)-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3“`The skeletal formula of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane is:“`CCCCCC(C)CC(C)C“`
IUPAC Nomenclature
The IUPAC rules for naming alkanes are as follows:
- The base name of the alkane is determined by the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain.
- The prefixes “ethyl” and “methyl” indicate the presence of ethyl and methyl groups, respectively.
- The numbers 5 and 2 indicate the positions of the ethyl and methyl groups on the parent chain.
The IUPAC name for 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane is 2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)octane.
Isomerism, Draw the structural formula of 5 ethyl 2 methyloctane
Structural isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane has the following structural isomers:
- 2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)octane
- 3-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)octane
- 4-methyl-3-(1-methylethyl)octane
Physical Properties
- -ethyl-2-methyloctane is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 176.2 °C, a melting point of
- 90.6 °C, and a density of 0.742 g/mL.
The physical properties of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane are influenced by its molecular structure. The branched-chain structure of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane results in weaker intermolecular forces than a straight-chain alkane with the same number of carbon atoms. This results in a lower boiling point and melting point for 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane.
Chemical Properties
-ethyl-2-methyloctane is a hydrocarbon, which means that it is composed of hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbons are generally unreactive, but they can undergo combustion, halogenation, and oxidation reactions.
Combustion
5-ethyl-2-methyloctane reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Halogenation
5-ethyl-2-methyloctane reacts with halogens to produce alkyl halides.
Oxidation
5-ethyl-2-methyloctane reacts with oxidizing agents to produce alcohols, ketones, and carboxylic acids.
Applications
-ethyl-2-methyloctane is used as a solvent, a fuel, and a lubricant. It is also used in the production of other chemicals, such as plastics and detergents.
Essential FAQs: Draw The Structural Formula Of 5 Ethyl 2 Methyloctane
What is the molecular formula of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane?
C10H22
How many structural isomers exist for 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane?
12
What is the boiling point of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane?
177.1 °C
Is 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane flammable?
Yes, it is highly flammable.
What are some applications of 5-ethyl-2-methyloctane?
It is used as a solvent, fuel additive, and in the production of synthetic rubber.