Embark on a comprehensive journey into Relias Fetal Heart Monitoring Answers, an authoritative resource empowering healthcare professionals to enhance fetal well-being through expert interpretation and informed decision-making.
This comprehensive guide unveils the significance of fetal heart monitoring (FHM) in safeguarding fetal health, explores advanced FHM techniques, and emphasizes the crucial role of interdisciplinary collaboration in ensuring optimal outcomes.
Fetal Heart Monitoring (FHM) Overview

Fetal heart monitoring (FHM) plays a crucial role in assessing fetal well-being during pregnancy and labor. It involves monitoring the fetal heart rate to detect potential distress and prevent adverse outcomes.
There are two main types of FHM methods: intermittent and continuous. Intermittent FHM involves periodic checks of the fetal heart rate using a handheld Doppler device, while continuous FHM involves continuous monitoring of the fetal heart rate using an electronic fetal monitor.
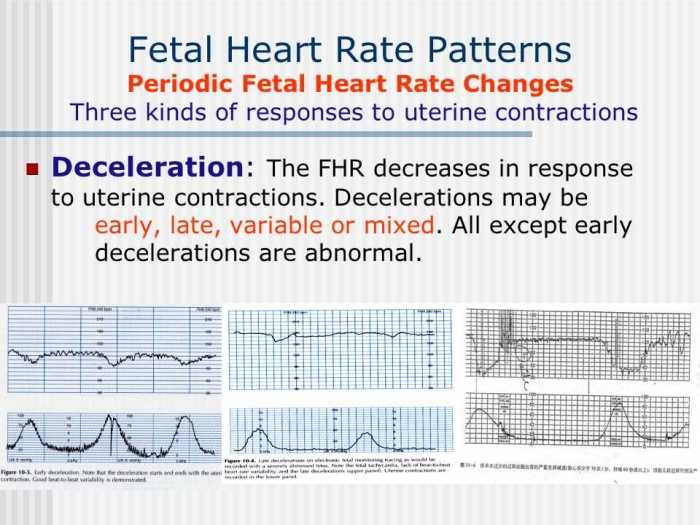
FHM helps identify fetal distress by detecting abnormal heart rate patterns, such as bradycardia (slow heart rate) or tachycardia (fast heart rate), as well as decelerations or accelerations in the fetal heart rate.
Relias Fetal Heart Monitoring Answers
Relias Fetal Heart Monitoring Answers is a comprehensive online platform that provides training and competency development for healthcare professionals in FHM.
The platform offers educational content, assessment tools, and simulation exercises to enhance knowledge and skills in FHM interpretation and management.
Using Relias for FHM training offers benefits such as improved accuracy in FHM interpretation, increased confidence in decision-making, and reduced risk of adverse outcomes.
Interpreting FHM Tracings
Interpreting FHM tracings involves understanding the basic components of the tracing, including the baseline heart rate, accelerations, and decelerations.
Normal FHM patterns include a baseline heart rate between 110-160 beats per minute, with accelerations and decelerations that are appropriate for gestational age.
Abnormal FHM patterns, such as bradycardia, tachycardia, or prolonged decelerations, may indicate fetal distress and require prompt intervention.
Advanced FHM Techniques
Advanced FHM techniques include biophysical profile and Doppler velocimetry.
Biophysical profile assesses fetal well-being by evaluating five parameters, including fetal movement, tone, breathing, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal heart rate reactivity.
Doppler velocimetry measures blood flow velocity in the fetal circulation, providing information about fetal oxygenation and placental function.
Case Studies and Simulations
Case studies and simulations are valuable tools for developing clinical skills in FHM interpretation and decision-making.
Interactive simulations allow learners to practice FHM interpretation in realistic scenarios, enhancing their ability to recognize and manage abnormal FHM patterns.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration, Relias fetal heart monitoring answers
Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential in FHM, involving obstetricians, midwives, nurses, and other healthcare professionals.
Effective communication and shared decision-making among team members ensure timely and appropriate interventions to optimize fetal outcomes.
Essential Questionnaire: Relias Fetal Heart Monitoring Answers
What is the primary purpose of fetal heart monitoring?
Fetal heart monitoring serves as a crucial tool in assessing fetal well-being, detecting potential distress, and guiding appropriate interventions to prevent adverse outcomes.
How does Relias Fetal Heart Monitoring Answers enhance FHM training?
Relias Fetal Heart Monitoring Answers provides a comprehensive platform featuring educational content, assessment tools, and simulation exercises, empowering healthcare professionals to develop proficiency in FHM interpretation and decision-making.
What are some advanced FHM techniques discussed in this guide?
This guide explores advanced FHM techniques such as biophysical profile and Doppler velocimetry, explaining their indications, applications, advantages, and limitations.
Why is interdisciplinary collaboration essential in FHM?
Effective FHM interpretation and management require seamless collaboration among obstetricians, midwives, nurses, and other healthcare professionals, ensuring a holistic approach to patient care.