In Big Ideas Math Geometry Chapter 9, students embark on an exploration of transformations, similarity, and congruence. This chapter delves into the fundamental concepts that govern the movement, shape, and size of geometric figures, laying the groundwork for a deeper understanding of geometry.
Through engaging examples and real-world applications, students will gain insights into the practical significance of these concepts in architecture, engineering, and design.
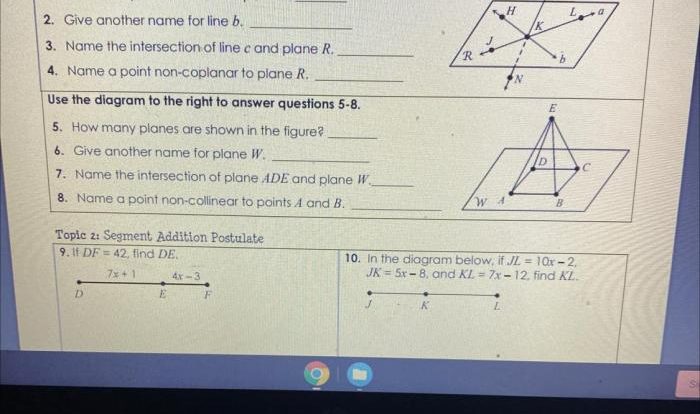
Chapter Overview
Chapter 9 of Big Ideas Math Geometry introduces the fundamental concepts of transformations, similarity, and congruence. It provides a comprehensive understanding of how geometric figures can be manipulated and analyzed, laying the groundwork for more advanced topics in geometry and its applications.
Transformations

Transformations are operations that move, rotate, or flip geometric figures. They preserve certain properties of the original figure, such as its size and shape. The chapter covers various types of transformations, including:
- Translations: Moving a figure from one point to another without changing its orientation or size.
- Rotations: Turning a figure around a fixed point.
- Reflections: Flipping a figure over a line.
Transformations are classified into two main categories:
- Rigid transformations: Preserve the size and shape of the original figure (e.g., translations, rotations).
- Non-rigid transformations: Alter the size or shape of the original figure (e.g., dilations, shears).
Similarity: Big Ideas Math Geometry Chapter 9

Similarity refers to figures that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Similar figures have corresponding angles that are congruent and corresponding sides that are proportional.
The chapter explores the properties of similar figures and introduces the concept of scale factor, which represents the ratio of the corresponding sides of two similar figures. Determining similarity involves using ratios and proportions.
Congruence
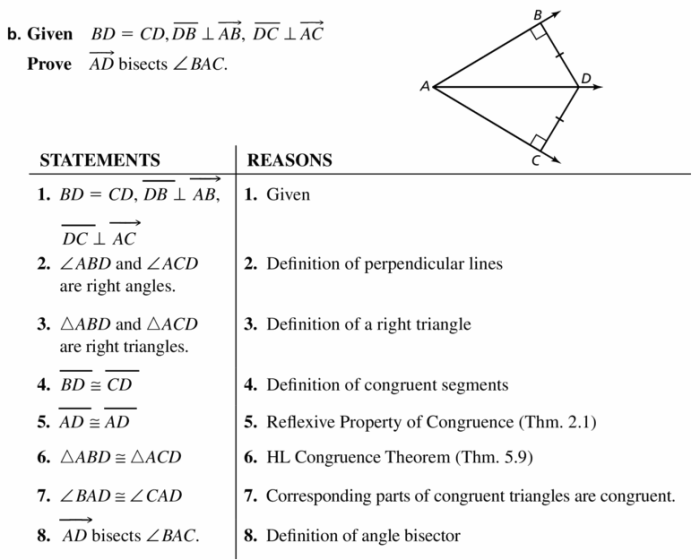
Congruence is a stronger form of similarity where figures have the same size and shape. Congruent figures have corresponding angles that are congruent and corresponding sides that are equal in length.
The chapter discusses the properties of congruent figures and the concept of rigid transformations, which preserve congruence. Congruence is essential for understanding geometric constructions and proofs.
Applications of Transformations
Transformations have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: Designing buildings and structures using geometric transformations.
- Engineering: Analyzing forces and stresses using geometric transformations.
- Design: Creating patterns, logos, and artwork using geometric transformations.
Understanding transformations is crucial for comprehending the world around us and solving problems in various fields.
Top FAQs
What are the different types of transformations covered in Chapter 9?
Chapter 9 covers translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations.
What is the concept of similarity?
Similarity refers to the relationship between two figures that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
How is congruence defined?
Congruence refers to the relationship between two figures that have the same shape and size.