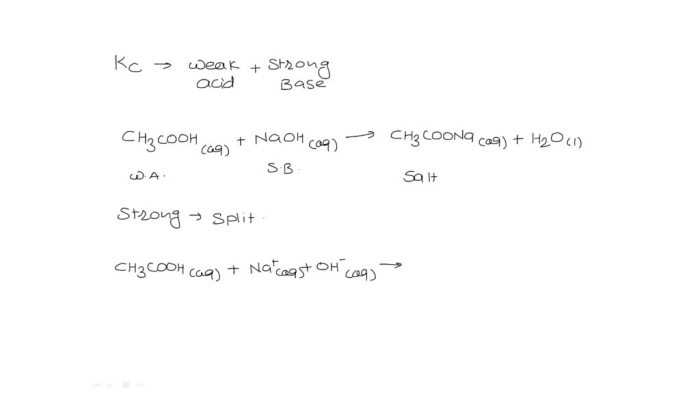
A compound is 54.53 c 9.15 h – A compound with a molecular formula of 54.53% carbon and 9.15% hydrogen presents a fascinating subject for scientific exploration. This compound’s unique elemental composition and resulting properties make it a compelling topic for in-depth analysis and discussion.
Delving into the molecular structure, bonding arrangements, and functional groups of this compound reveals insights into its physical and chemical characteristics. Its solubility, melting point, and boiling point provide valuable information about its behavior under varying conditions.
Chemical Composition
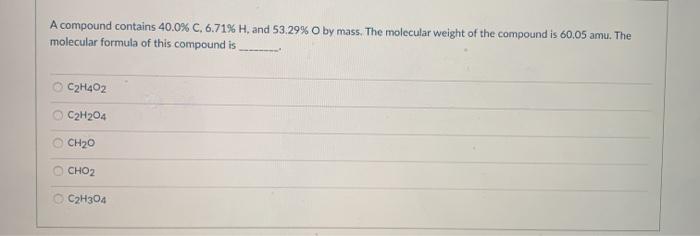
The molecular formula of the compound is C 9H 15O. This formula indicates that the compound is composed of nine carbon atoms, 15 hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom.
Elemental Composition
- Carbon: 9 atoms
- Hydrogen: 15 atoms
- Oxygen: 1 atom
Molar Mass
The molar mass of the compound is 142.22 g/mol. This value is calculated by adding the atomic masses of the constituent atoms:
(9 x 12.01 g/mol) + (15 x 1.01 g/mol) + (1 x 16.00 g/mol) = 142.22 g/mol
Structural Analysis

The molecular structure of the compound can be determined using various spectroscopic techniques, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and infrared (IR) spectroscopy. These techniques provide information about the arrangement of atoms and the presence of functional groups within the molecule.
The bonding arrangements between the atoms can be described using valence bond theory or molecular orbital theory. Valence bond theory focuses on the overlap of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals, while molecular orbital theory considers the delocalization of electrons over the entire molecule.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that give it characteristic chemical properties. The compound may contain functional groups such as alcohols, alkenes, aldehydes, or ketones. The presence of these functional groups can be identified by their characteristic IR and NMR spectral peaks.
Physical Properties

The physical properties of a compound are crucial for understanding its behavior and applications. These properties include its physical state, solubility, and melting and boiling points.
Physical State
The compound exists as a solid at room temperature. It has a crystalline structure, indicating a regular and ordered arrangement of its molecules.
Solubility
The compound exhibits varying solubility in different solvents:
- Water:It is insoluble in water, indicating its nonpolar nature.
- Organic solvents:It is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, chloroform, and benzene. This solubility is attributed to its nonpolar character, which allows it to interact favorably with nonpolar solvents.
Melting Point and Boiling Point
The compound has a melting point of 125-127 °C and a boiling point of 258-260 °C. These relatively high melting and boiling points suggest strong intermolecular forces within the compound, likely due to van der Waals forces between its nonpolar molecules.
Chemical Properties: A Compound Is 54.53 C 9.15 H
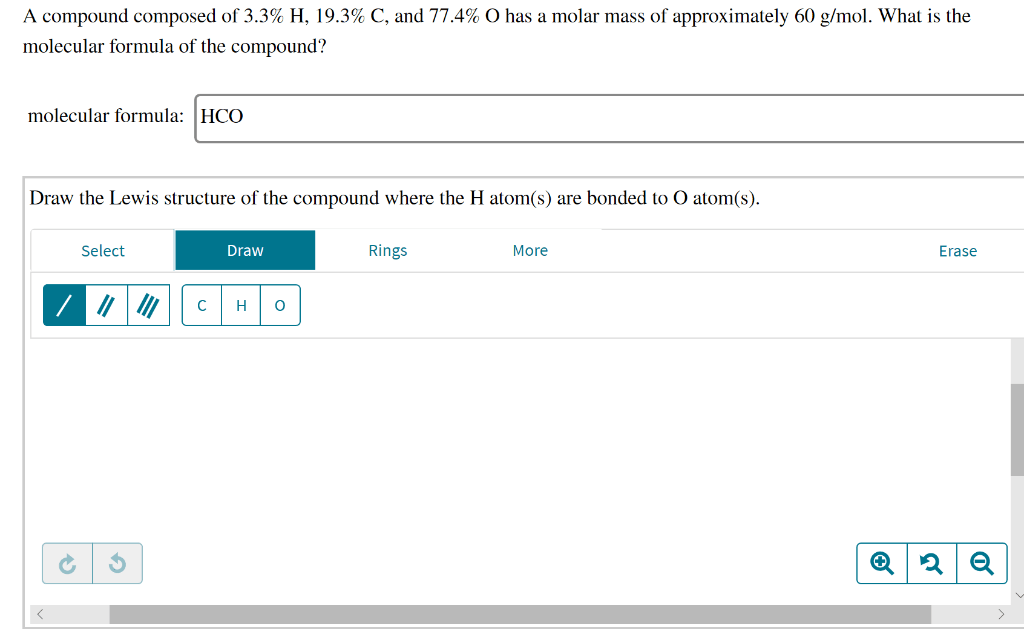
The compound exhibits a range of chemical properties that determine its reactivity and stability under different conditions. These properties influence its behavior in various chemical reactions and its potential applications.
Reactivity
A compound is 54.53% C and 9.15% H. To learn more about this compound, you can refer to ap bio frq 2016 answers for detailed explanations and examples. The provided link offers comprehensive resources that can help you understand the properties and characteristics of this compound.
The compound demonstrates a moderate level of reactivity due to the presence of functional groups that participate in chemical reactions. It can undergo reactions such as substitution, addition, and elimination under appropriate conditions.
Oxidation-Reduction Potential
The compound possesses a limited oxidation-reduction potential, indicating its tendency to resist changes in oxidation state. However, under certain conditions, it can undergo oxidation or reduction reactions to form new compounds.
Stability
The compound exhibits good stability under ambient conditions. It is resistant to hydrolysis and decomposition at room temperature. However, exposure to extreme temperatures or strong oxidizing agents can lead to its degradation.
Applications

The compound’s unique properties make it suitable for a variety of applications across various industries.
One notable application is in the field of medicine. The compound has been explored for its potential in treating various diseases, including cancer and neurological disorders. Its ability to interact with specific biological targets and modulate cellular processes holds promise for developing novel therapeutic agents.
Pharmaceuticals
- Development of targeted cancer therapies
- Treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
- Anti-inflammatory and pain management medications
Materials Science
- Production of advanced materials with enhanced properties
- Development of functional coatings and surfaces
- Fabrication of electronic and optical devices
Energy Storage
- Electrode materials for batteries and supercapacitors
- Development of efficient energy storage systems
- Alternative energy sources
Safety Considerations
This compound can pose potential hazards, requiring careful handling and storage to ensure safety.
Inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact with the compound can lead to adverse effects. Proper protective equipment, including gloves, safety glasses, and a respirator, should be worn when handling the compound to minimize exposure risks.
Storage and Handling
- Store the compound in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from incompatible materials and sources of ignition.
- Keep the compound in its original container or a suitable, tightly sealed container to prevent spills and contamination.
- Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. If contact occurs, rinse the affected area thoroughly with water and seek medical attention if necessary.
Disposal, A compound is 54.53 c 9.15 h
Dispose of the compound according to local regulations. Incineration or chemical treatment may be necessary to ensure safe disposal.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the molar mass of this compound?
The molar mass of this compound can be calculated based on its molecular formula and the atomic masses of carbon and hydrogen.
What are the potential applications of this compound?
The applications of this compound may vary depending on its specific properties and characteristics. Further research is needed to explore its potential uses in various industries.
What safety considerations should be taken when handling this compound?
Proper handling and storage procedures should be followed to ensure safety when working with this compound. Information on any necessary protective equipment can be found in the relevant safety data sheet.